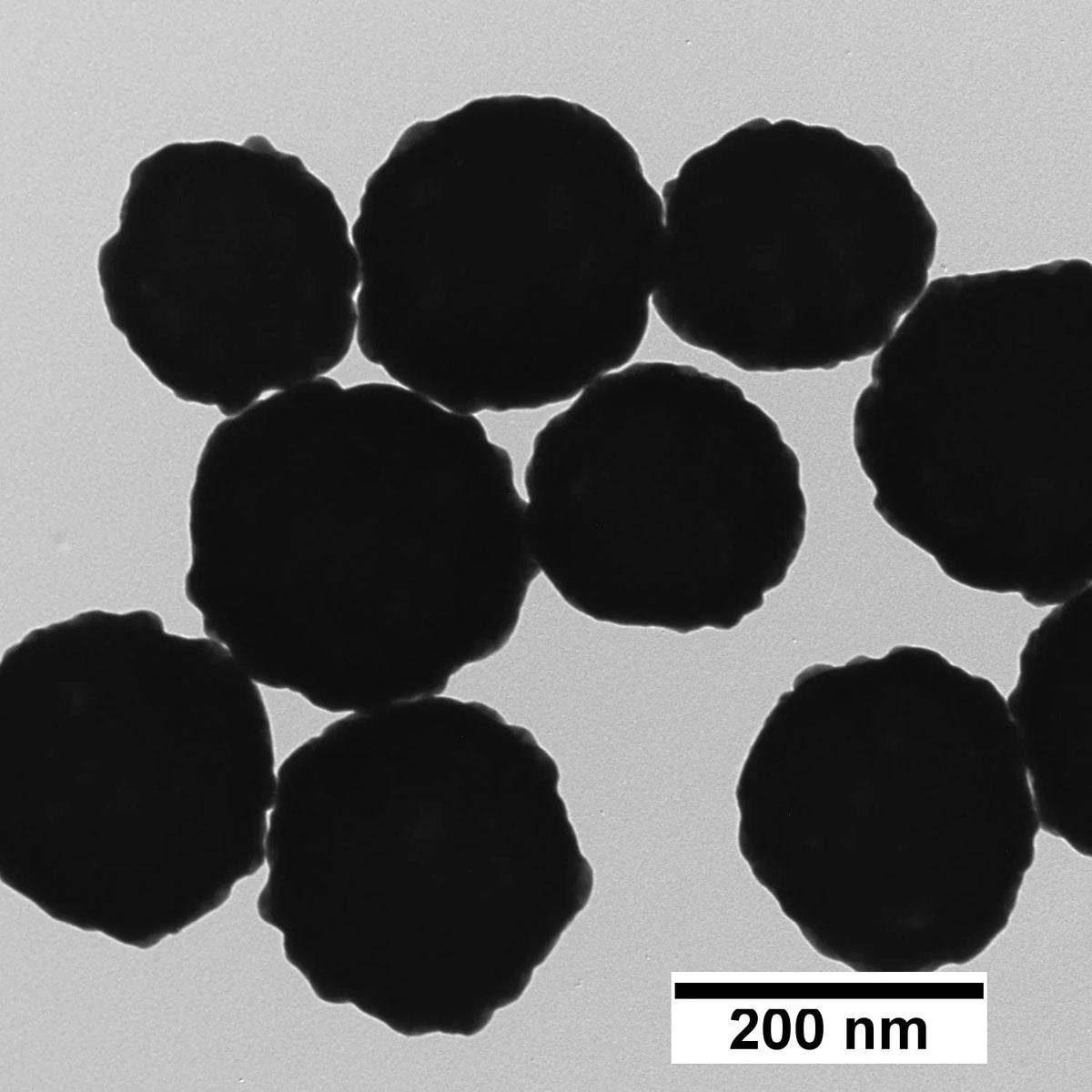
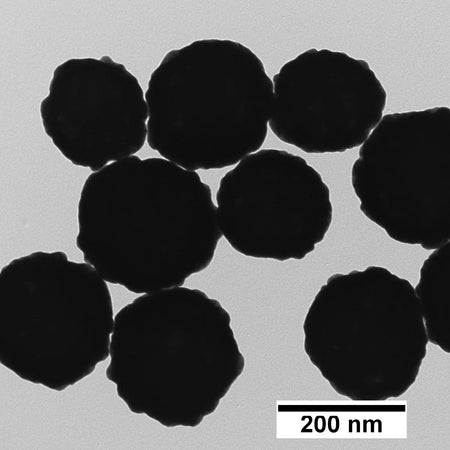
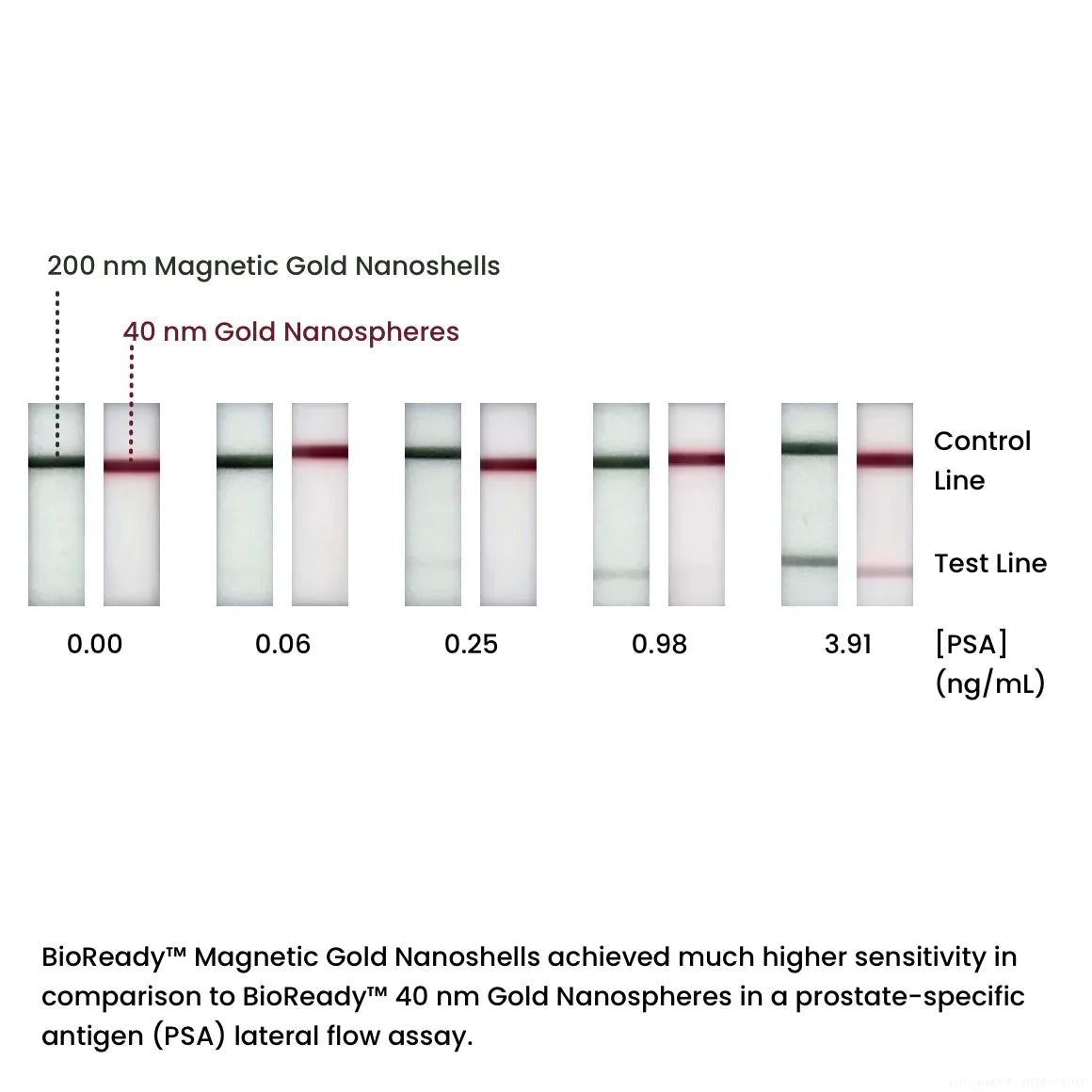
200 nm Magnetic Gold Nanoshells
Customers outside of the US & Canada: please visit your local distributor’s website to purchase this item using its SKU, or contact us here. Thank you!
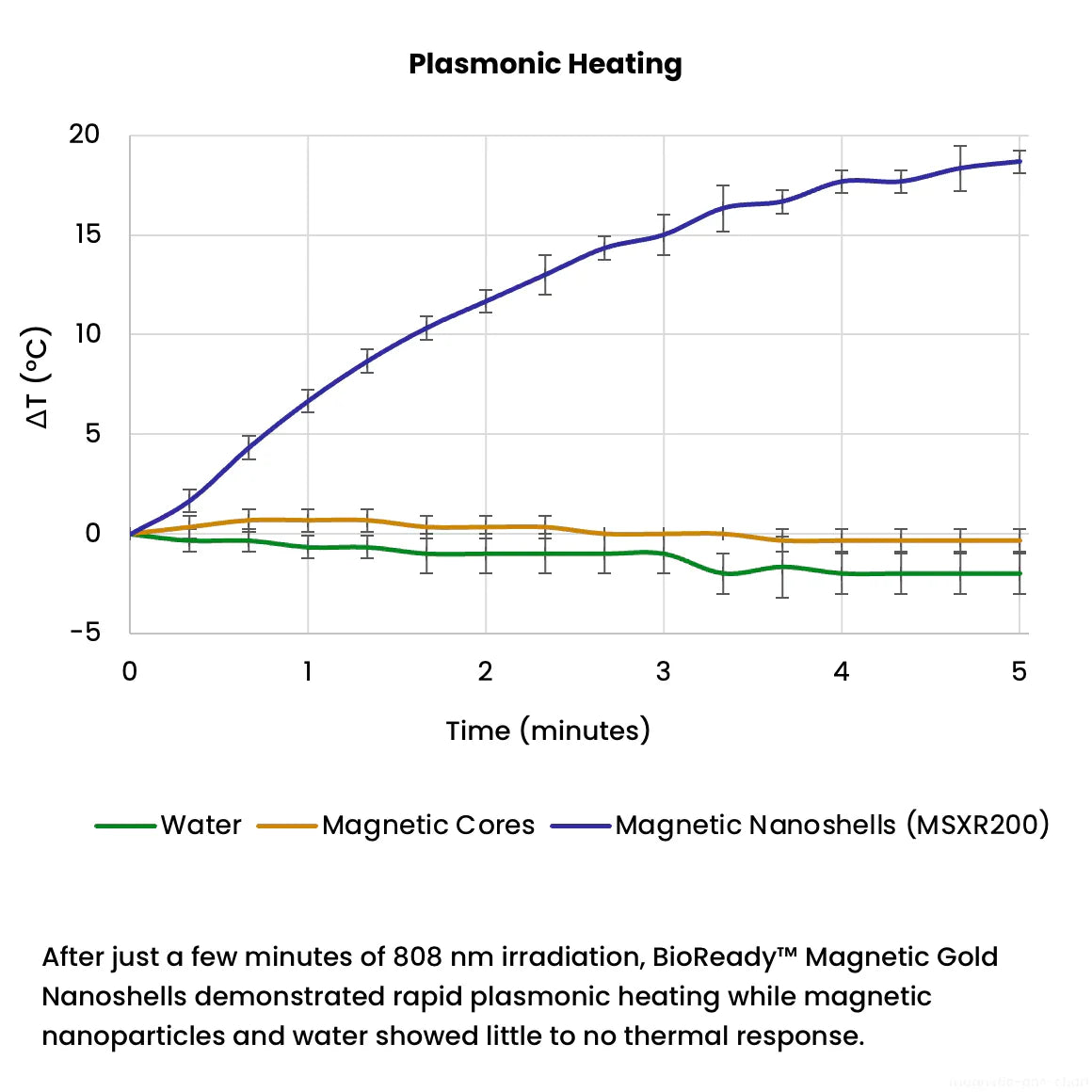
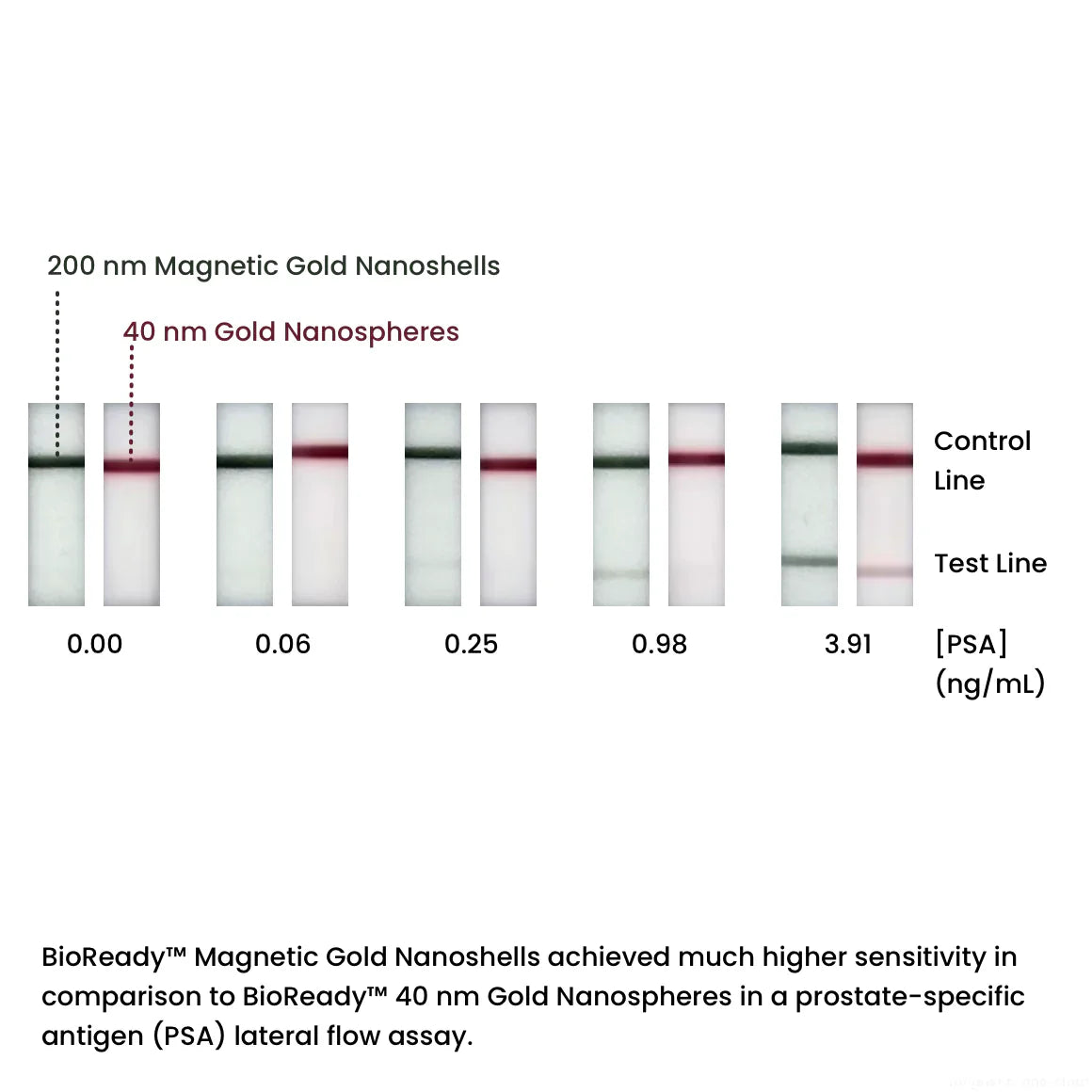
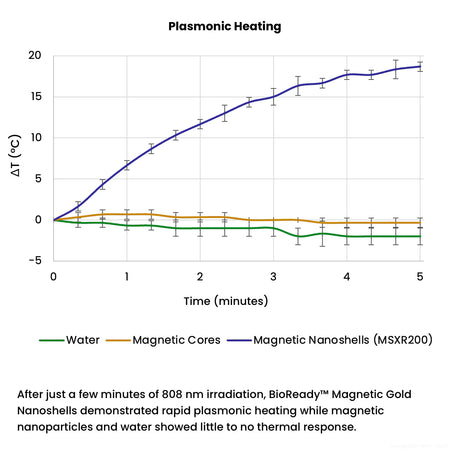
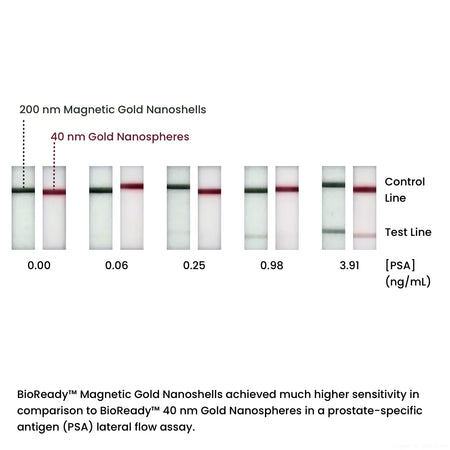
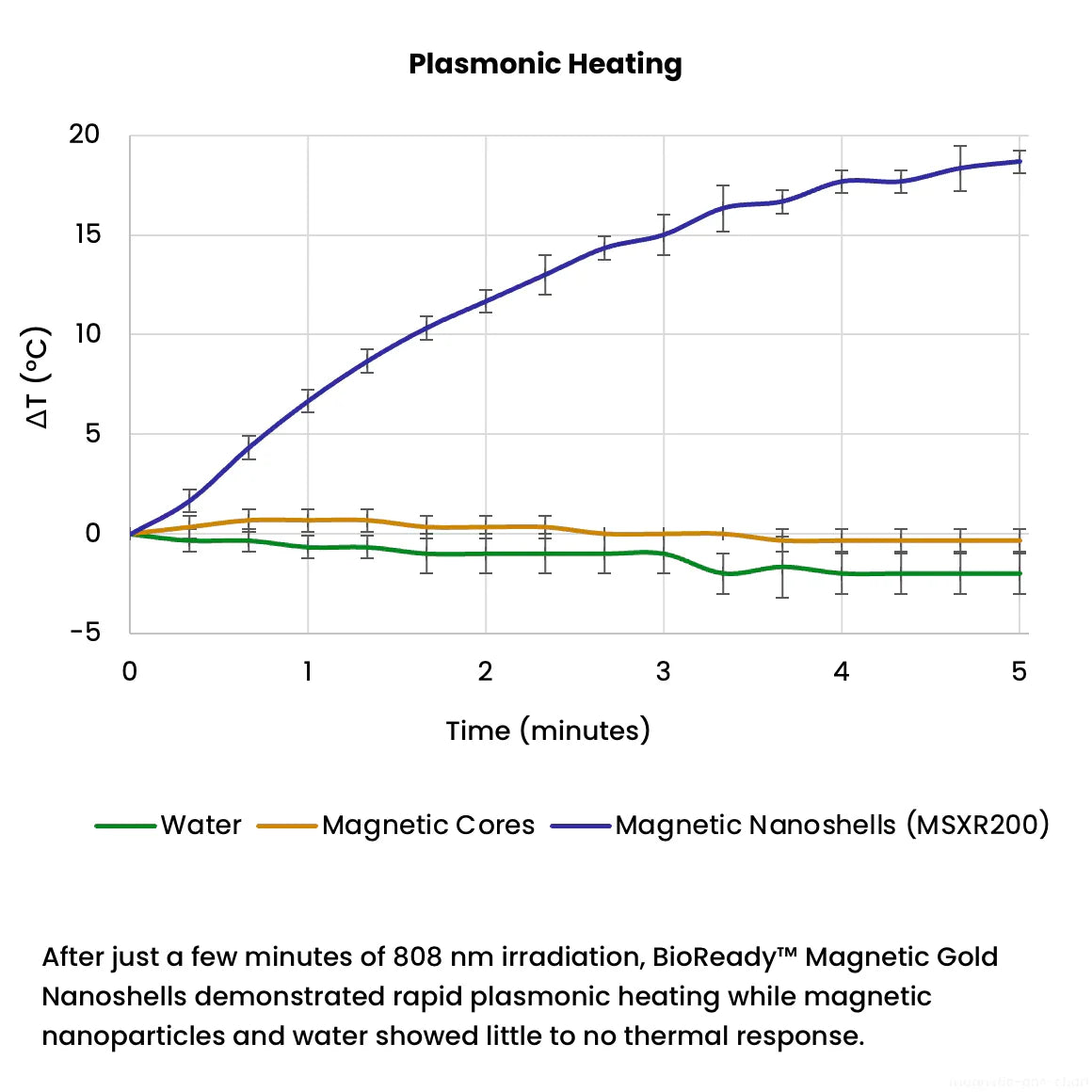
200 nm magnetic gold nanoshells are useful in a variety of therapeutic and diagnostic applications such as biosensors, lateral flow assays, SERS, drug delivery, and photothermal therapy. These nanoparticles have a superparamagnetic core that enables easy manipulation such as separation or concentration, and the plasmonic optical properties of a gold nanoshell.
BioReady Magnetic Gold Nanoshells utilize a carboxyl ligand (lipoic acid) that is covalently bound to the metal surface enabling subsequent covalent conjugation. Antibodies and other amine-containing biomolecules efficiently bind to carboxyl gold nanoshells using EDC-NHS chemistry to make highly stable conjugates. Review our conjugation protocol or contact our experts for support.
nanoComposix provides high quality, monodisperse, and aggregation-free nanomaterials. All our products are supplied with a batch-specific Certificate of Analysis including characterization data such as TEM, DLS, Zeta, and UV-Vis.
Intended for Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Contact us for custom formulations, ISO 13485/cGMP compliant materials, or bulk supply requirements.
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Surface | Carboxyl |
| Description | Covalently bound. Conjugatable surface. |
| Solvent | 0.02 mM potassium carbonate |
| Surface chemistry | Lipoic acid |
| Specifications | |
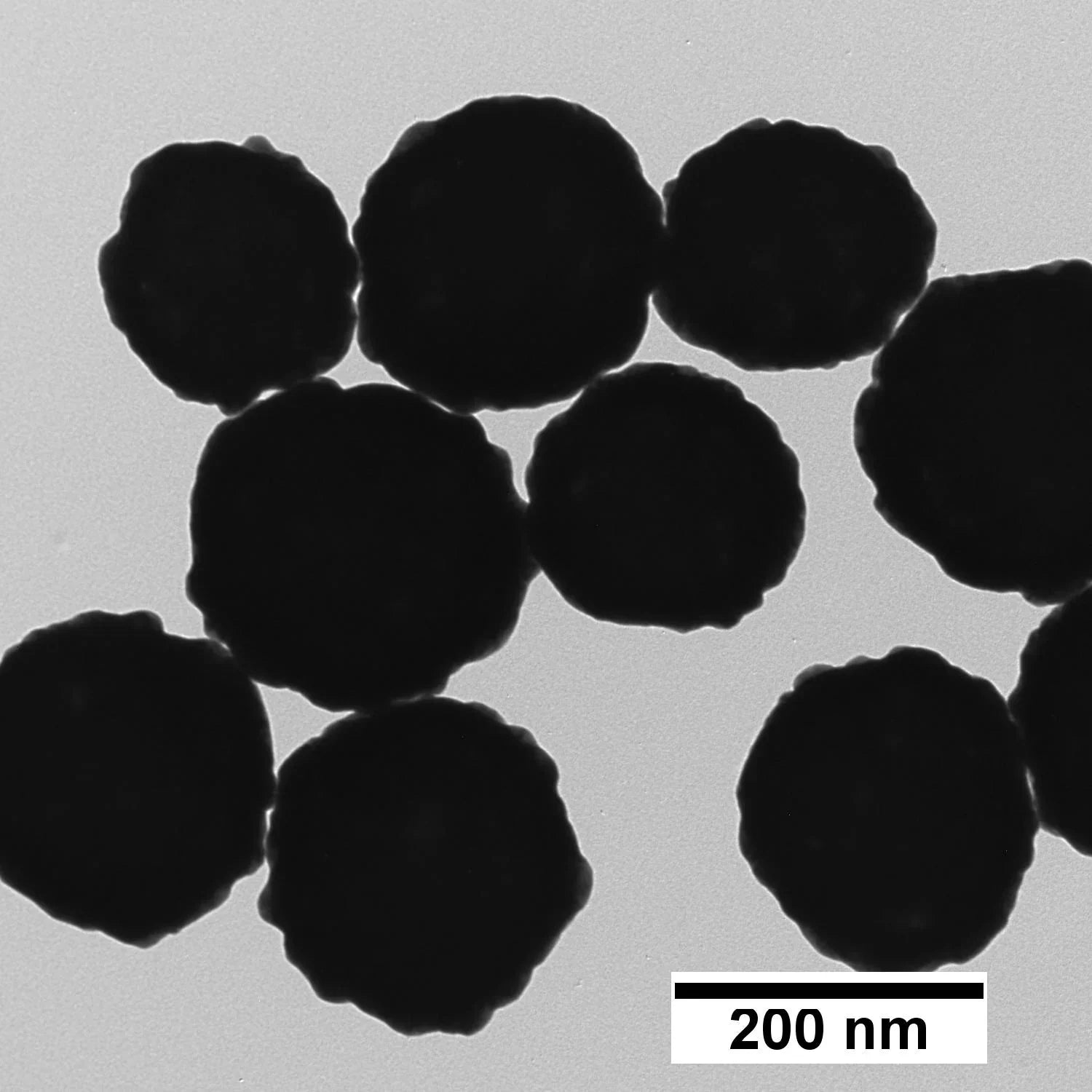
| TEM Diameter | 205 ± 20 nm |
| CV | ≤ 15% |
| Documents | |
| Example Certificate of Analysis (CoA) | Download |
| Safety Data Sheet (SDS) | 10 OD (BioReady) |
| Storage & Handling | Download |
| Protocols | Antibody Purification BioReady 200 nm Carboxyl Magnetic Gold Nanoshell Covalent Conjugation Tutorial video: Covalent Coupling of Antibodies to Carboxyl Gold Nanoparticles ↗ |
| Expected Ranges | |
| Zeta potential | ≤ –40 mV |
| Peak wavelength (λmax) | 780–890 nm |