Nanomaterials exhibit a variety of unique and useful optical properties that can differ significantly from the properties exhibited by the same bulk material. By carefully controlling the size, shape, and surface functionality of nanoparticles, a wide range of optical effects can be generated with many useful applications. An optical response in a nanomaterial can be created through several different mechanisms, depending on the nanomaterial's size, composition, and arrangement, and each method may provide certain benefits depending on the target application.
Below are several case studies across different application areas, highlighting how high-quality nanomaterials make the difference in achieving superior optical performance and device reliability.
Cell Gap Spacers
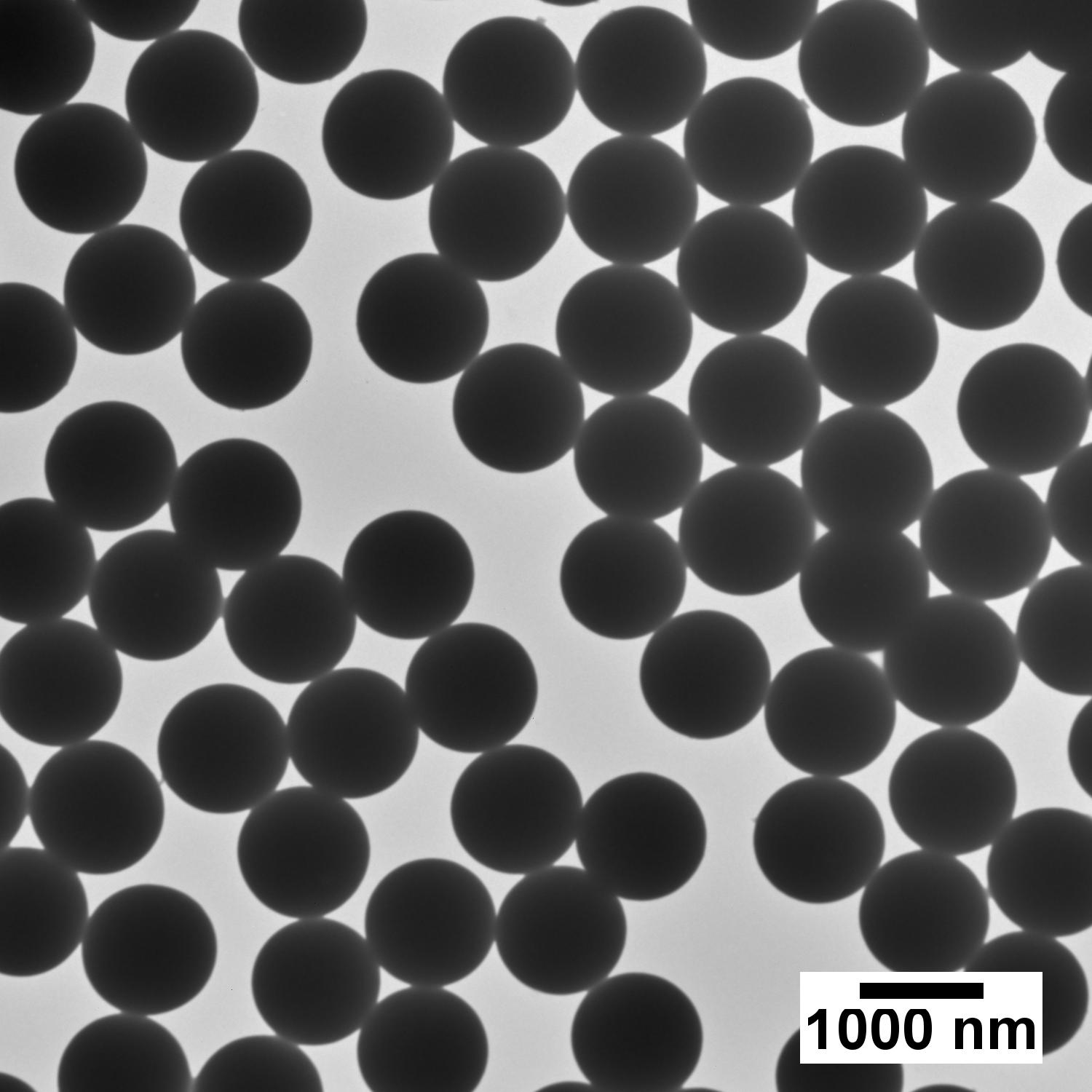 In display architectures, silica nanoparticles can play a vital role as cell gap spacers, where their monodispersity ensures consistent cell thickness for uniform optical paths and image clarity. Their mechanical strength and optical transparency maintain structural integrity without compromising visual performance, enabling more reliable and precise panel assembly.
In display architectures, silica nanoparticles can play a vital role as cell gap spacers, where their monodispersity ensures consistent cell thickness for uniform optical paths and image clarity. Their mechanical strength and optical transparency maintain structural integrity without compromising visual performance, enabling more reliable and precise panel assembly.
High-quality nanomaterials, characterized by narrow size distribution, high sphericity, and exceptional purity, are essential to maintain uniform liquid-crystal cell gaps. Even small deviations in particle size or shape can cause optical defects, non-uniform brightness, and alignment errors that degrade display quality.
Case Study
When a display manufacturer compared silica nanoparticles from multiple suppliers, nanoComposix materials stood out for their consistency and performance. The precise spherical morphology, high purity, and tightly controlled particle size enabled the customer to achieve superior cell gap uniformity across their display prototypes.
Transparent Conductive Films (TCFs)
 In touchscreens and flexible display systems, silver nanowires provide the essential balance of high electrical conductivity and optical transparency. Their interconnected nanowire networks enable efficient charge transport while minimizing light scattering, resulting in responsive, high-clarity devices that can endure repeated bending.
In touchscreens and flexible display systems, silver nanowires provide the essential balance of high electrical conductivity and optical transparency. Their interconnected nanowire networks enable efficient charge transport while minimizing light scattering, resulting in responsive, high-clarity devices that can endure repeated bending.
The quality of the nanowires, including uniform diameter, high aspect ratio, and low junction resistance, is critical for reliable electrical and optical performance. Poorly synthesized nanowires can lead to elevated resistance, higher haze, and mechanical failure during flexing.
Literature Example
Tao et al. (2021) optimized silver nanowire-based transparent conductive films to achieve high optical clarity with low haze. By precisely controlling silver nanowire diameter and aspect ratio, they produced sparse yet continuous conductive networks. The resulting films exhibited ~80% transmittance, ~75 Ω/sq sheet resistance, and <2% haze, outperforming conventional indium tin oxide( ITO). The low haze was attributed to reduced light scattering from slender, uniform nanowires and optimized spatial distribution. This work highlights how morphology engineering of silver nanowires enables superior transparency–conductivity balance and enables low-haze, flexible electrodes in next-generation optoelectronic devices.
Tao, J.; Liu, N.; Li, S.; Shi, J.; Ji, S. Structural manipulation of silver nanowire transparent conductive films for optoelectrical property optimization in different application fields. Thin Solid Films 2021, 729, 138679.
Tunable optical properties
Plasmonic nanomaterials, such as gold and silver, exhibit precisely tunable optical signatures that enable advanced photonic applications.
Gold Nanoparticle Spectra

Silver Nanoparticle Spectra

Enhanced display technologies
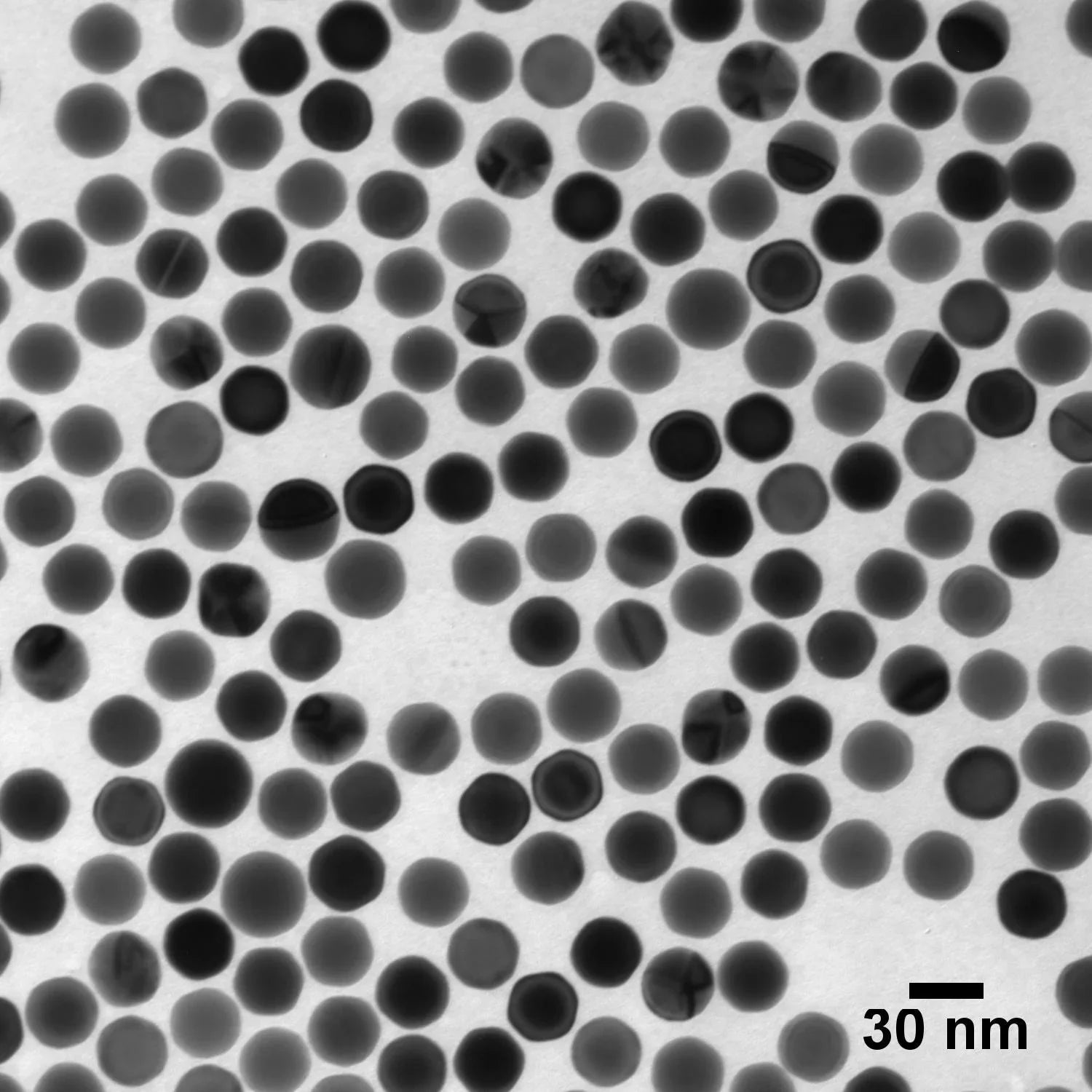 To achieve richer color output and improved brightness, plasmonic nanomaterials such as gold and silver nanoparticles are increasingly integrated into optical architectures. Their tunable localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPRs) enable precise spectral control, allowing engineers to design displays with higher color purity, sharper contrast, and reduced power consumption. Gold nanoparticles provide spectral tuning across the visible range, while silver nanoparticles deliver stronger resonance with lower optical loss—critical for high-definition and miniaturized display systems.
To achieve richer color output and improved brightness, plasmonic nanomaterials such as gold and silver nanoparticles are increasingly integrated into optical architectures. Their tunable localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPRs) enable precise spectral control, allowing engineers to design displays with higher color purity, sharper contrast, and reduced power consumption. Gold nanoparticles provide spectral tuning across the visible range, while silver nanoparticles deliver stronger resonance with lower optical loss—critical for high-definition and miniaturized display systems.
Here, nanomaterial qualities such as uniform particle size and shape directly govern color saturation and brightness. Tight control over particle size and morphology enables enhanced color and improved efficiency.
Case Study
A mobile device manufacturer approached us to help realize their vision for advanced coating technologies. We developed plasmonic materials that distributed uniformly across polycarbonate substrates, producing coatings with vivid, homogeneous color that remained stable even after extended exposure to intense UV light. The result was a durable, visually consistent finish ideal for next-generation consumer electronics applications.
Anti-Reflective, Anti-Refractive Coatings
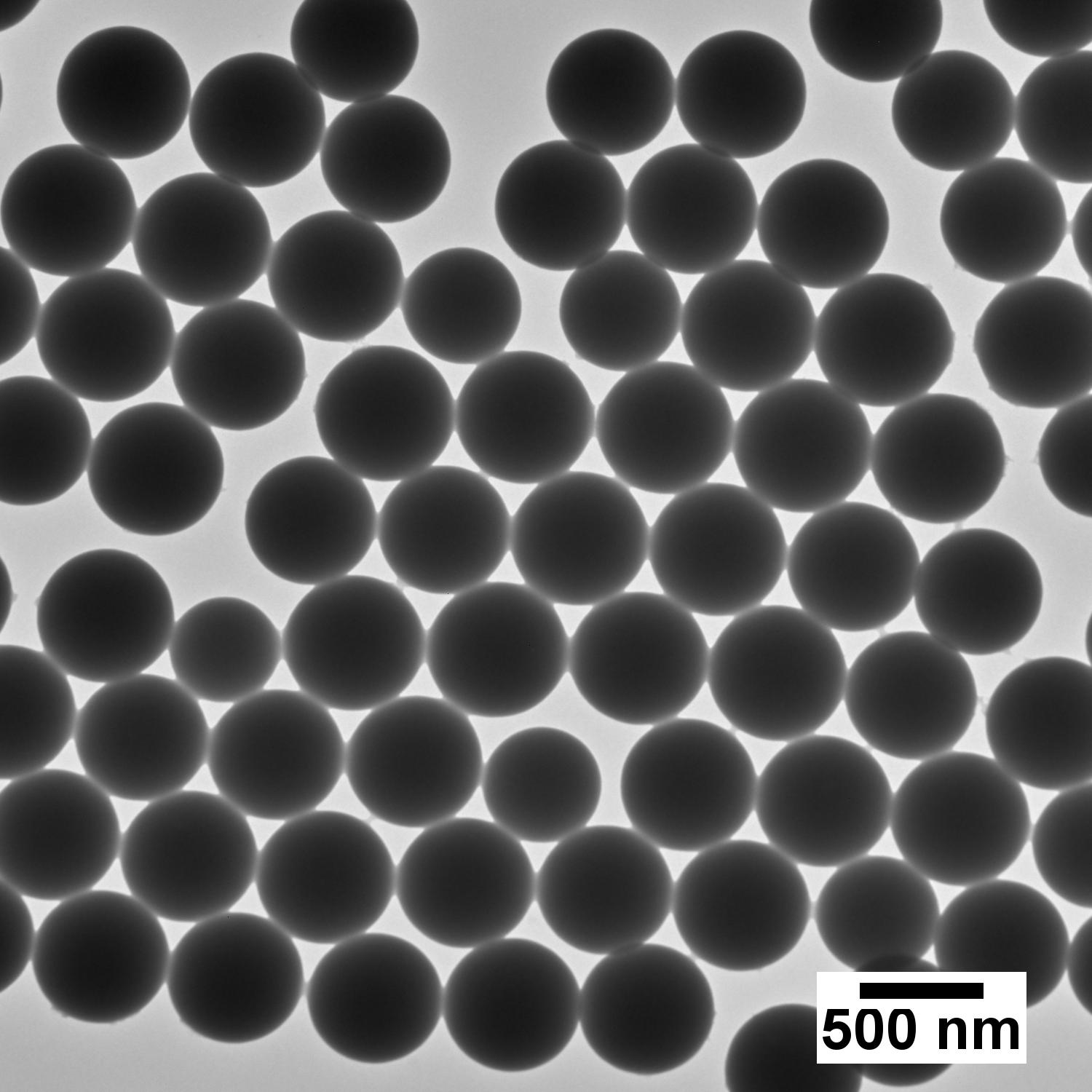 For optical coatings, silica nanoparticles are valued for their low refractive index and excellent light transmittance, which reduce glare and reflection losses. These properties enhance luminance and color fidelity in display modules or optical lenses, ensuring consistent performance across varying light environments.
For optical coatings, silica nanoparticles are valued for their low refractive index and excellent light transmittance, which reduce glare and reflection losses. These properties enhance luminance and color fidelity in display modules or optical lenses, ensuring consistent performance across varying light environments.
When silica nanoparticles of high purity and uniformity are used, they form denser, smoother coatings with more predictable refractive indices. This quality ensures stable, durable anti-reflective performance and minimizes scattering or surface defects that degrade optical transmission.
Literature Example
Zhang et al. (2014) demonstrated a highly effective broadband antireflective coating using 100 nm monodisperse silica nanospheres assembled into compact monolayers on glass. Coating both sides of the substrate achieved 99% transmittance at 560 nm, greatly enhancing light transmission over bare glass. The optical peak position was tunable across the UV–visible range by adjusting deposition parameters, enabling precise control of antireflective behavior without loss of film quality. The study shows that uniform, size-controlled silica nanospheres enable simple, scalable, and efficient broadband AR coatings suitable for solar cells, windows, displays, and optical lenses.
Zhang, Z.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X. Tuning the Peak Position of Subwavelength Silica Nanosphere Broadband Antireflection Coatings. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 361.
From the mechanical precision of silica spacers to the optical finesse of gold plasmonics, the message is clear across applications: nanomaterial quality defines performance. Whether the goal is sharper images, brighter displays, or more flexible touchscreens, it is the uniformity, purity, and structural control of the nanomaterials that transform innovative concepts into commercially reliable technologies.
Explore our nanomaterial portfolio for your optical engineering applications.



